
DR.S.ARAVAMUDHAN
http://www.ugc-inno-nehu.com/
BIODATA
CONTACT INFO
Curriculum Vitae/Resume
&n bsp; http://nehuacin.tripod.com
http://www.ugc-inno-nehu.com/
webpages_list
 DR.S.ARAVAMUDHAN http://www.ugc-inno-nehu.com/ |
BIODATA CONTACT INFO Curriculum Vitae/Resume &n bsp; http://nehuacin.tripod.com http://www.ugc-inno-nehu.com/ webpages_list |
|
This Syllabus has been designed for a Course with a Title: ' MAGNETIC RESONANCE SPECTROSCOPIC TECHNIQUES ' as part of the Proposal made to the UGC under the Innovation Programme of the UGC. Such of those instructors who wish to avail this farmework are hereby requested to place on record with the UGC about the usefulness of these materials. CLICK HERE to download an introductory article on NMR as a Tool for Structure Determination CLICK HERE to download a presentation file on a comparitive enumeration on the Molecular nad Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Techniques uploaded on Thursday, September 25, 2008 5:52 AM Click Here for an article on using ppt files in Classrooms. In a Course which is meant for the discussion of "Structure Determination by NMR" the following presentation files can be helpful to choose from and highlight the relevant NMR technical aspects at appropriate stages. Links below added on Saturday, March 29, 2008 at 7:41AM
Some of the Contents of the above Presentation Files have been reorganized and presented with additional features in the subsequent workshop on FT NMR at the SAIF, NEHU, Shillong. Those presentation files have benn appropriately made into smaller sizes and thus were conveniently converted into VIDEO FORMAT using "WONDERSHARE PPT to WMV" Converter Software. These VIDEO movies have been uploaded to the account of Dr. S. Aravamudhan This course content is drafted specifically to introduce and explain the basics of NMR Phenomenon and Technique.
At this stage the advances made in NMR as a tool for structure detrmination are not narrated, but the scope of this content includes these advances
(without specifically mentioning the specific names of such technical aspects) by specially stressing the basic aspects which are getting an importance at the stage of
trying to grasp the advanced techniques.Purpose had been to emphasize and highlight such topics in basic Science streams which are covered at a
much earlier stages of educational levels.This is essentially providing a strong foundation for enabling a quick grasp as and when the front line reports
are available on this technique. ---This text inscribed on Saturday, March 29, 2008 at 9:21AM
|
| AAS #3A Curriculum Structure and Course Contents Subject-Discipline: CHEMISTRY - Physical Chemistry Course Title: THE MAGNETIC-RESONANCE SPECTROSCOPIC TECHNIQUE |
|
1. Mathematical Techniques - I 2. Mathematical Techniques - II 3. Description of the Magnetic Resonance Phenomena & Detection techniques 4. Theoretical Descriptions Using Quantum Mechanical Tools 5. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy(NMR) 6. Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Spectroscopy(EPR) 7. Comparison of NMR & EPR Methods 8. Nuclear Quadrupole Resonance 9. Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy & Optical Spectroscopy - A comparison 10. Detailed consideration of the Recent Advances in the NMR Spectroscopic Techniques Provisional (optional) Lecture-hours for tutorials and demonstration classes Total Number of Lecture HOURS |
3 3 5 10 4 2 2 2 9 43 2 45 |
| 2.when there are relevant materials a "hotlink" is provided to download and view them at the appropriate spot in the running text of the syllabus 3. HOTLINKS to appropriate webpages (.html or .htm)appear on the rightmost column |
|
|
| |
| |
Revision of Trigonometric sine and cosine functions - Argument for sine and cosine in units of radians or degrees - Angular velocity ; Angles as product of angular velocity and time - angular velocity and angular frequency - A graphical (pictorial) depiction of sine and cosine functions in terms of the argument in units of degrees and units of time - Constant-Maximum-Amplitude sine and cosine functions depicted as rotating Constant-Amplitude-Vectors when the argument is a product of angular velocity (frequency) and time. Linear Simple Harmonic Motion describing the instantaneous variation of the Amplitude-component of a rotating Constant-Amplitude vector. | |
| Real and Imaginary parts of an exponential (complex) function : Euler's expansion , Euler's relation and its significance mathematical expression for rotations of constant-amplitude vectors - sense of rotation : Clockwise and Anticlockwise , Right and Left handedness - An unambiguous sign convention, for the sense of rotation, while expressing these by Euler's relation. | ||
| Electromagnetic Radiation, its characteristic mathematical forms in theoretical descriptions: the linear and circular polarizations explained on the basis of Euler?s relation for the Exponential functions ::- An exercise in generating various curves and shapes with corresponding mathematical equations - sine and cosine functions and their products with exponentially decaying functions and step functions - all of them expressed approximately with respect to the same time axis. |
|
|
| |
| Angular Momentum : the angular momentum operators , spin operators , single spin operators and product spin functions , commutation rules for spin operators - Exponential Operators : commuting and non-commuting operators (as the exponents) in Exponetial Operators - the expansions for Exponential Operators for evaluation of matrix-elements | ||
| Matrices , products of matrices , commutation rules for matrices: Matrix multiplications - Spins, spin basis functions for angular momentum operators, matrix representation of the angular momentum operators | ||
|
|
First order differential equations and solutions : A revision to prepare for familiarity to Bloch?s Equations and their solutions for spin-ensembles |
|
|
| |
| Angular momentum and associated Magnetic Moments : Gyromagnetic ratios of nuclei and electron - Influence of Magnetic fields on Classical Bar Magnets distinction from the magnetic moments associated with quantizable angular momentum components - Forces and Torques on the magnetic moments: precession in Magnetic Fields : Precession frequency,effect of the applied electromagnetic radiation fields,The RESONACE Effect. | dipole NMR.pdf |
|
| Zeeman splitting of degenerate spin sublevels : Energy of Separation due to zeeman interaction : Energy of electromagnetic-radiation photons and resonance condition: polarization of electromagnetic radiations and quantum mechanical selection rules for the magnetic resonance effect. | ||
| Individual spin and the Ensemble of spins -practical consideration for NMR experiments & displaying detected Magnetic Resonance : Magnetic moment and Magnetization, spin polarization, population differences - single spin precesiion descriptions , Magnetization and Relaxation times : Definition of quantitative spin polarizations and magnetizations - detection of magnetic resonance : Resonant Circuits and Sample coils , induction and absorption methods of detection. |
|
| A MS PowerPoint file (file_size= 483 KB) for a one-hour lecture on descriptions of PULSED NMR & relevant for the contents of this unit |
|
| |
Spin wave functions , Spin operators , Representations of the Spin Operators and the basis functions,single-spin-operator algebra,commutation rules : descriptions for the spin ensemble and the effect of magnetic fields on the spin system | effects |
| |
Spin Hamiltonian, The zeeman term : The necessity for rotating reference frame: the Zeeman Hamiltonian in the laboratory Fixed Frame and the Rotating reference Frame - spin-spin and spin -orbit interactions for the electron spins and the corresponding Hamiltonians - The considerations for the Nuclear spin-spin interactions | |
| |
An introduction to the Density-matrix descriptions of the spin-ensembles | |
| |
Description of evolution of spin systems influenced by perturbing Hamiltonians (internal and external) : RF perturbations and use of exponential operators to describe the evolution of the various terms in the Hamiltonian | |
| |
Effect of RF pulses : Description using exponential (rotation) operators - the CW technique and the PULSE Technique descriptions.
Click for *nehulink_movie.wmv* A 5 mts. movie file on Pulsed FT NMR; file size 28MB This link added on Friday, March 28, 2008 at 3:42 PM |
|
| |
|
|
| |
Resonance Conditions for NMR : Multinuclear NMR Considerations | ||
| |
Specific considerations of Proton , Carbon , Nitrogen and Phosphorous nuclei from the point of view of NMR Spectroscopy | Proton, Carbon |
|
| Chemical Shifts as the experimentally measurable parameter due to the Shielding effects in Atoms and Molecules | |||
| |
Spin-Spin Coupling parameter as an aid in the NMR Spectroscopy | ||
| |
A Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectrum described | ||
| |
Considerations of electronic molecular structures for their manifestations in the NMR Spectroscopy | ||
| |
NMR spectra : Analysis of spectra and assignments | ||
| V.9 & V.10 |
Examples from APPLICATIONS
|
NMR of Hydrogen Spectroscopy NOW |
|
|
| |
| |
The g-shifts , the Hyperfine coupling parameters | |
| |
Spectroscopic Considerations as different from the NMR technique | |
| |
Supplementary informations to and from NMR spectroscopy of Paramagnetic molecules | |
| |
The typical transition metal ions studied by EPR - the organic Free radicals |
|
| |
|
| |
Appearance of NMR and EPR Spectra ; the differences in the spectrometer detection techniques |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CLICK HERE to down load (a MS WORD document) an introductory article on describing NQR Phenomenon. The content of the above article has been presented at the NMRS2008 link included on March 29, 2008 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Electromagnetic Spectrum and the regions of Optical spectroscopy : the reasons for the various Optical Spectroscopic Characteristics and the corresponding electromagnetic regions. | Electro- magnetic radiation Spectrum |
| |
The energy level separations , magnitudes and the causes of level separations (splittings) , the differences in Boltzmann factors , populations and population differences of various spectroscopic techniques ; their relative sensitivities , utility considerations | Spectros- copy Analytical tool |
|
|
IN NMR SPECTROSCOPIC TECHNIQUE |
|
| |
NMR : the Wide-line and High Resolution NMR | |
| |
Sample characteristics : amount of samples required , sensitivity and resolution and the S/N considerations - advantages of High field Spectrometers : Spectrometer characteristics for liquid H R NMR | |
| |
Solid-State Wide-Line NMR : Second Moments and the line-width considerations | |
| |
Multiple pulse techniques ( and multiple coherences) in Liquid State HR NMR | |
| |
Selective Polarisation Transfer and related techniques for heteronuclear NMR Sensitivity | |
| |
Multi dimensional liquid state HR NMR | |
| |
The various multidimensional NMR experiments listed out : illustrations with examples | |
| |
A brief description of the pulse sequences and their effect on spin systems for liquid state and solid state HR NMR
|
|
| |
Selected Applications of structural parameter determinations using Solid State NMR and Liquid State NMR ( the liquid state NUCLEAR OVERHAUSER TECHNIQUE) |
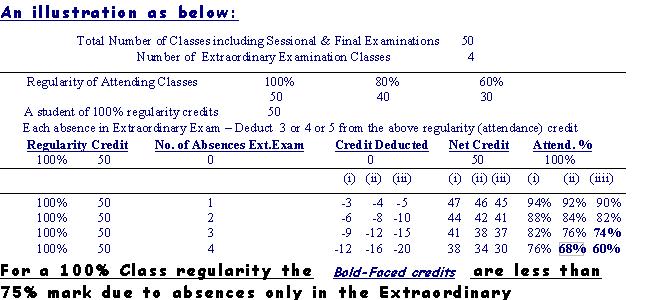
| It is intended to have three sessional and one final examinations for grading purposes. Further it is being proposed to have three or four unconventional tests/exams like the open Book examinations OR discuss a typical question paper in the class-room and specify a time duration where this question paper would be distributed to the students and answer as a conventional exmination paper. These would not be included in the markings for the Grading but absences at these additional Exams would cost the students heavily in attendance markings by including a negative attendance for defaults at these Exams. It could be that in a 45 Class attendance each absence in the Additional Exams would cost the students Three to Five classes in attendances and in the stipulated number of attendance-requirements the students would not be eligible for final certificate even if they had regularly attended other lecture-classes and Gradable Exams. By such examination methods the Examiner and the Instructor can try to find out the difficulties of the students by the mock exams which are mandatory like the lecture classes, with better importance. |
 CLICK HERE for an article on a related topic:Absent and Accounted For: Absenteeism and Cooperative Learning |